White dwarfs — the superdense, slowly cooling embers left behind when stars like our sun die — are usually quiet cosmic relics. A rare few, however, are anything but.
In recent years, astronomers analyzing data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia spacecraft identified a handful of white dwarfs hurtling through the Milky Way at breakneck speeds of up to 1,240 miles per second (2,000 kilometers per second). That’s fast enough to zip from New York to Los Angeles in under two seconds — and to escape the galaxy entirely.
These so-called hypervelocity white dwarfs have puzzled astronomers since their discovery in 2018. Their extreme speeds suggest they were launched by powerful, violent events, but no single theory has been able to explain both their breakneck velocities and their puffed-up, overheated appearances — perhaps until now.
A new study co-led by Hila Glanz of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology may offer the most compelling explanation of hypervelocity white dwarfs yet. Using detailed computer simulations, the researchers modeled what happens when two white dwarfs in a tight binary system spiral together in a merger.
“It’s like a puzzle,” Glanz told Space.com in a recent interview. “We want to see what kind of pieces we can add to the story.”
The results, detailed in a paper published Aug. 19 in the journal Nature Astronomy, successfully recreated not only the dramatic ejection speeds observed by Gaia but also many of the unusual physical characteristics of these stellar cannonballs.
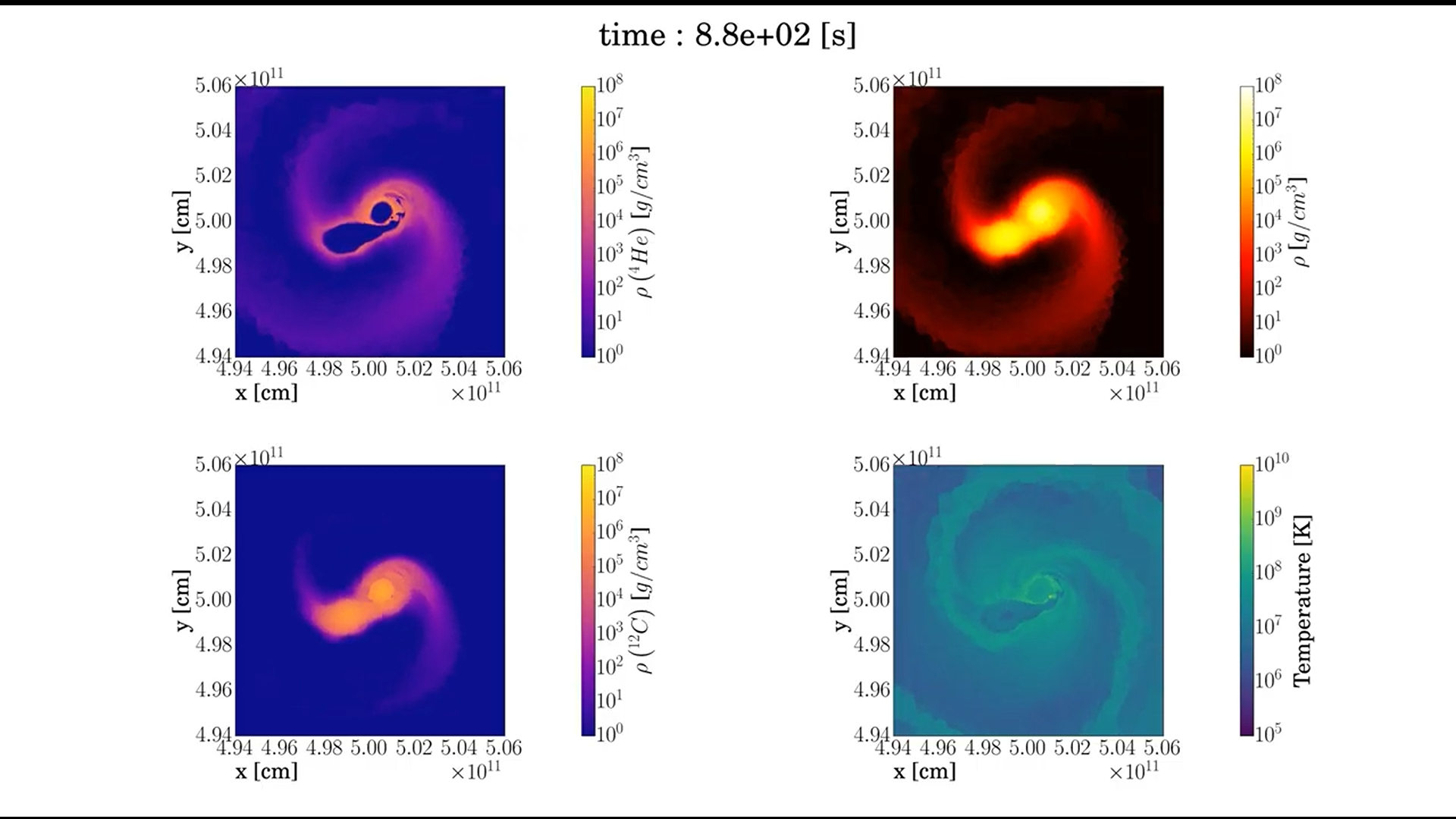
The researchers focused on a merger of two hybrid white dwarfs — stellar remnants with carbon-oxygen cores wrapped in thick shells of helium, likely shaped by earlier interactions with companion stars. In the simulation, the lighter star is pulled inward and begins to be shredded by its heavier partner. As they interact, friction and compression heat the surface of the more massive white dwarf, eventually igniting its helium shell in a violent burst.
That first explosion sends a shockwave racing around the star’s outer layers, according to the new study. When it converges on the opposite side, it compresses and heats the core, triggering a second detonation — this time in the carbon–oxygen core, which causes the primary star to explode in what astronomers call a thermonuclear supernova.
“It completely explodes,” said Glanz. “There’s nothing left.”
With its partner obliterated, the partially disrupted companion, now unbound, is flung outward at tremendous speed, propelled by both the blast and the immense orbital energy built up during the final moments of the supernova.
The simulation traced the system for about 17 minutes after the explosion, showing how it naturally produces both high ejection speeds and the inflated, luminous profiles seen in observed hypervelocity white dwarfs.
And because the explosion is relatively faint, its debris disperses quickly, leaving behind little trace of a supernova. That, too, matches current observations of white dwarfs flying through space without any visible remnants nearby, the study reports.
The prevailing theory — the D6 scenario (short for “dynamically driven double-degenerate double-detonation”) — posited that a massive white dwarf detonates after minimal mass transfer, leaving the companion intact. But this model struggles to reconcile both the extreme velocities and the puffed-up appearances seen in hypervelocity white dwarfs, according to the new study.
Glanz’s merger model, by contrast, shows that even a relatively low-mass primary can produce a fast-moving remnant, thanks to a partial disruption. And because the resulting supernova is faint, its remnants fade fast, leaving the ejected white dwarf looking like a solitary wanderer.
“We did not really know what we were gonna get,” said Glanz. “When we saw the results, it actually fitted this long-standing question of how these hypervelocity white dwarfs formed. It was super cool.”
The findings also shed light on the origins of Type Ia supernovae, the bright stellar explosions that serve as standard candles for measuring cosmic distances, and that forge many of the elements essential for life, including iron.
Rather than pointing to a single origin, the study suggests that hypervelocity white dwarfs may arise from a diverse “zoo” of stellar interactions and explosions, including faint supernovae triggered by double detonations in mergers like the one Glanz’s team simulated.
Still, Glanz emphasizes that this is only part of the picture. Future sky surveys, such as those soon to be carried out by the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, could help put these theories to the test. If astronomers catch such a merger and explosion in real time, it could help confirm the violent process that sends these stellar cannonballs flying across the galaxy.
“It’s not like we solved everything,” she said. “We need to collect more pieces of the puzzle [and] continue exploring this zoo.”


5 Comments
https://shorturl.fm/ZR5Mh
https://shorturl.fm/DBeJG
https://shorturl.fm/akZJ4
https://shorturl.fm/f0Q2F
y1xtlm