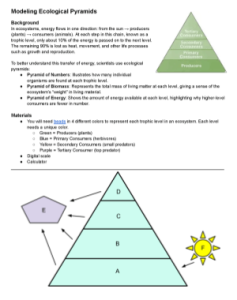
Looking for a way to include hands-on activities in an ecology unit? I’ve struggled with student engagement in this unit, mainly because so many of the concepts involve models. In this activity, students use beads to model the three types of ecological pyramids: pyramid of numbers, pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy.
Each group gets a bag filled with colored beads to represent the trophic levels. One bead represents the top predator, or tertiary consumer. 5 beads for the secondary consumers, 15 for the primary consumers, and 30 for the producers.
First, students count each bead to illustrate a pyramid of numbers. They will see that in the ecosystem there are more producers than consumers. As you move up trophic levels, the number of consumers decreases, illustrating that an ecosystem can only have a small number of tertiary consumers.
In the second task, students weigh each group of beads (organized by color to represent organisms). This is how students will construct the pyramid of biomass. This also gives students experience with using scales and the tare function. They place the beads in weighing boats, press tare to zero the scale, and then record the mass of the beads. This illustrates that biomass decreases as you go up the trophic levels.
In the final task, students use a calculator to determine the amount of energy at each level. They start with the assumption that the producers capture 10,000 J of energy from the sun. To calculate the transfer of energy, divide that number by 10. This represents the amount of energy that is lost to heat at each trophic level.
In the reflection section, students answer questions about their models and ecosystems. They apply what they have learned to real-world ecosystems and design a pyramid of numbers to represent a forest or ocean ecosystem.
Related Resources
Case Study: Sea Otters and Kelp Forests – Explore the history of sea otter hunting and their recovery
Trophic Cascades – Uses an interactive activity at HHMI to explore trophic cascades in a variety of ecosystems
Ecology Case Study – The Wolves of Isle Royale – population decline and reintroduction of wolves
Exploring Limiting Factors and Carrying Capacity – read ecology scenarios and identify density dependent and density independent factors
Random Sampling – estimate a population of “sunflowers”


1 Comment
https://shorturl.fm/Evnq0